This article explores how RFQ-Based Decentralized Exchanges (DEXes) are changing the game on blockchains, going beyond traditional liquidity pools to have a profound impact on how people trade in the decentralized space.
The most common ways in which users trade in Decentralized Finance (DeFi) are on Decentralized Exchanges (DEXes) and DEX aggregators, which leverage automated market makers (AMMs) to source liquidity. But there are better ways; let's explore the RFQ.
Let's break down the finance jargon and make it more accessible!#
In the world of finance, there are two terms you might come across: OTC and RFQ. OTC stands for "over-the-counter," and it's like buying medicine without a doctor's prescription. But in finance, it means trading that happens directly between two parties, not on formal exchanges like the stock market.
Now, let's talk about RFQ, which stands for "Request for Quote." Imagine you want to buy something, and you're not sure where to get the best price. With RFQ, you ask different sellers for their prices. It's like shopping around for the best deal. This type of trading can happen directly between you and a seller (that's the OTC part) or through a formal exchange that helps both parties through the RFQ process.
And guess what? These terms aren't just for cryptocurrencies; they're used in traditional financial markets too! So, when you hear OTC and RFQ, just think of it as a way people buy and sell things directly or by asking for quotes to find the best deal. Easy, right?
Here's the breakdown for newcomers:#
With the advent of blockchain technology, RFQs (Request for Quotes) can now take place directly on a blockchain. This means that people can submit their RFQ orders and have them matched directly on the blockchain itself, without the need for a centralized exchange.
Now, you might wonder how this is distinct from traditional decentralized exchanges (DEX). In most DEXs, trading relies on automated market makers (AMMs) and liquidity pools that anyone can contribute to. However, the approach I just mentioned involves a more direct RFQ process on the blockchain, offering a different way for users to trade without depending on liquidity pools. It's all about exploring various methods within the realm of blockchain-based trading!
Key Advantages of On-Chain RFQ Trading:#
1. No Surprises with Prices:#
On some decentralized exchanges, you might see something called "slippage," like a prediction of how your trade might affect the price. With RFQ on-chain, the price you see is the price you get; it won't change after you've started the transaction. No surprises!
2. Gas included in the quote:#
On regular decentralized exchanges, when you make a trade, you often need to pay for the transaction using the native blockchain token (like ETH or MATIC). But with RFQ on-chain, the cost of the transaction (gas) is already included in the quote. So, you know exactly what you're paying without needing extra tokens for fees.
3. Protection Against Unwanted Actions:#
Transactions on the blockchain are visible to everyone, and sometimes bad actors try to manipulate them. With RFQ on-chain, there's protection against these manipulations, known as Miner Extractable Value (MEV) attacks. This helps to keep your trades secure and free from unwanted actions.
In simpler terms, trading RFQ on-chain means clear prices, no surprise fees, and added security against certain types of attacks. It's a more straightforward and secure way to trade on the blockchain!
Differences Between Regular DEX and RFQ:#
In a regular decentralized exchange (DEX), anyone can join and be a part of the liquidity pools, which are managed by Automated Market Makers (AMMs). On the other hand, in RFQ, Professional Market Makers (PMMs) supply liquidity and also set the prices for assets. This setup prevents unexpected price changes and protects against certain types of attacks.
In traditional DEXes, a smart contract acts as an intermediary, but in RFQ, there's no such middleman. Another distinction is that regular DEXes don't include transaction fees (gas) in the asset prices, whereas RFQ projects do.
How RFQ Works:#
- A user makes a request on the exchange.
- A market maker (a professional) proposes a price to the user.
- The user can either accept or decline the offer.
- If accepted, a smart contract facilitates the transfer of tokens between the user and the market maker. Importantly, the smart contract doesn't hold onto the funds; it simply ensures the transaction happens securely.
In simpler terms, RFQ is like a direct conversation between a user and a professional market maker, ensuring clear prices and secure transactions without the need for a smart contract intermediary.
Now, let's delve into an overview of some exciting projects within the RFQ-based DEXes.
Hashflow
Hashflow is a DEX operating across multiple chains, such as Ethereum, Arbitrum, Avalanche, BNB Chain, Optimism, Polygon, and Solana. In a matter of seconds, users can seamlessly trade various digital assets.
Hashflow utilizes an innovative intent-based smart order routing system, ensuring traders access optimal prices and a vast liquidity pool exceeding $8 billion. This platform empowers users to trade any token effortlessly, providing a comprehensive solution for diverse digital asset trading needs.
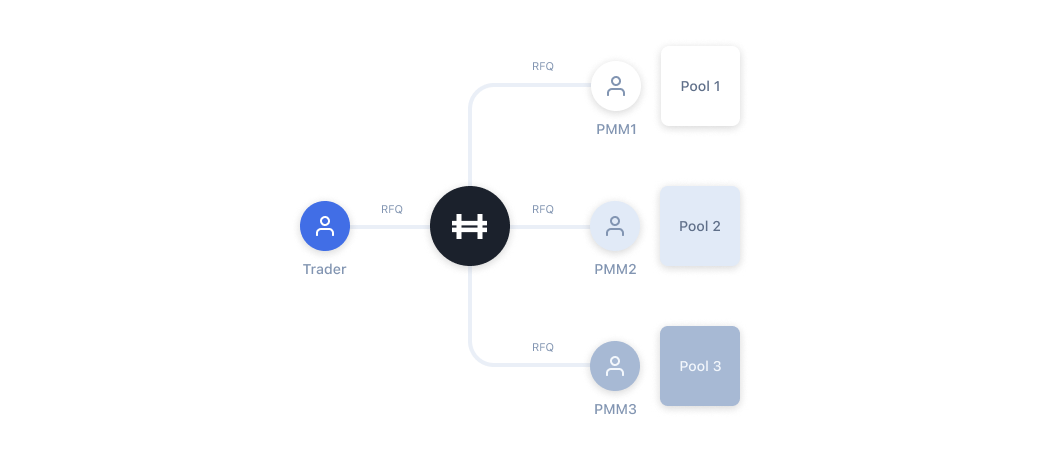
Hashflow's RFQ Model
Hashflow: Empowering Market Makers for Dynamic Trading Success#
Hashflow revolutionizes market maker dynamics by introducing a streamlined Request for Quote (RFQ) model, ensuring efficient quoting for quicker market interactions. Market makers leverage dynamic off-chain pricing functions backed by cryptographic signatures, enabling sophisticated pricing strategies.
Hashflow takes a unique approach that gives market makers powerful tools. They can now consider a wide range of off-chain data, like past asset prices and volatility indicators, making their decisions on pricing assets more informed and effective. It’s not your typical platform; Hashflow goes above and beyond, providing market makers with exceptional advantages to succeed in the ever-changing world of digital asset trading.
Bebop
So, what exactly is Bebop? Bebop operates in the decentralized exchange (DEX) arena with a distinctive approach. In the realm of cryptocurrency, where definitions can be a bit unclear, here’s the scoop: A DEX, technically, functions on a decentralized network, allowing users to trade without intermediaries like centralized exchanges. And, indeed, Bebop checks those boxes. Operating on smart contracts, it ensures users maintain complete control of their funds at all times, fitting the DEX definition.
However, there’s more to the Bebop story. While it brings all the benefits of traditional DEXes—think permissionless, transparent, and trustless—Bebop goes further. Positioned as a decentralized exchange sourcing liquidity from private market makers, think of it as a liquidity aggregator, adding an extra layer to enhance the trading experience.
How does this work exactly? Below, we’ve created a visual for how the RFQ on-chain model operates with multiple private liquidity providers (also known as market makers).
Here is how it works:#
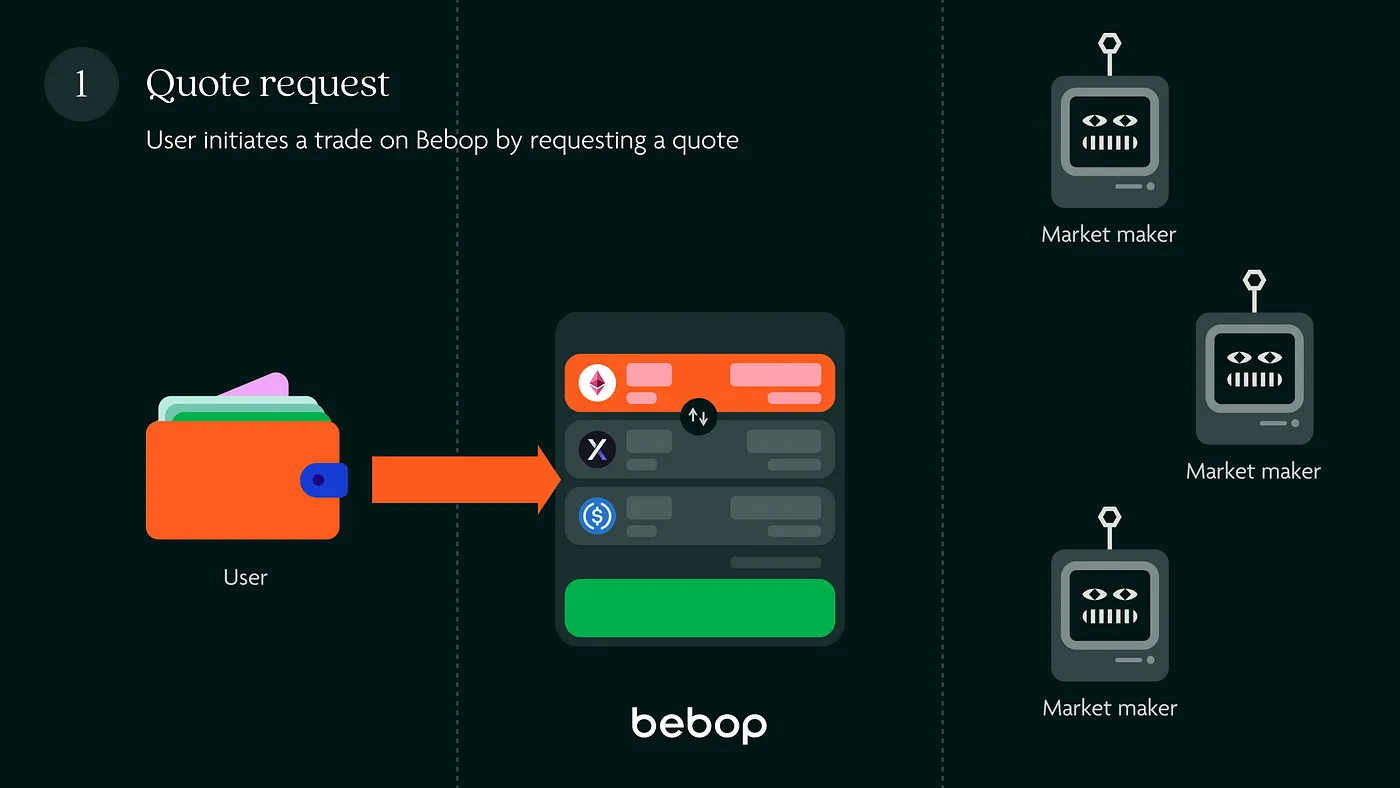
Step 1: Quote request#
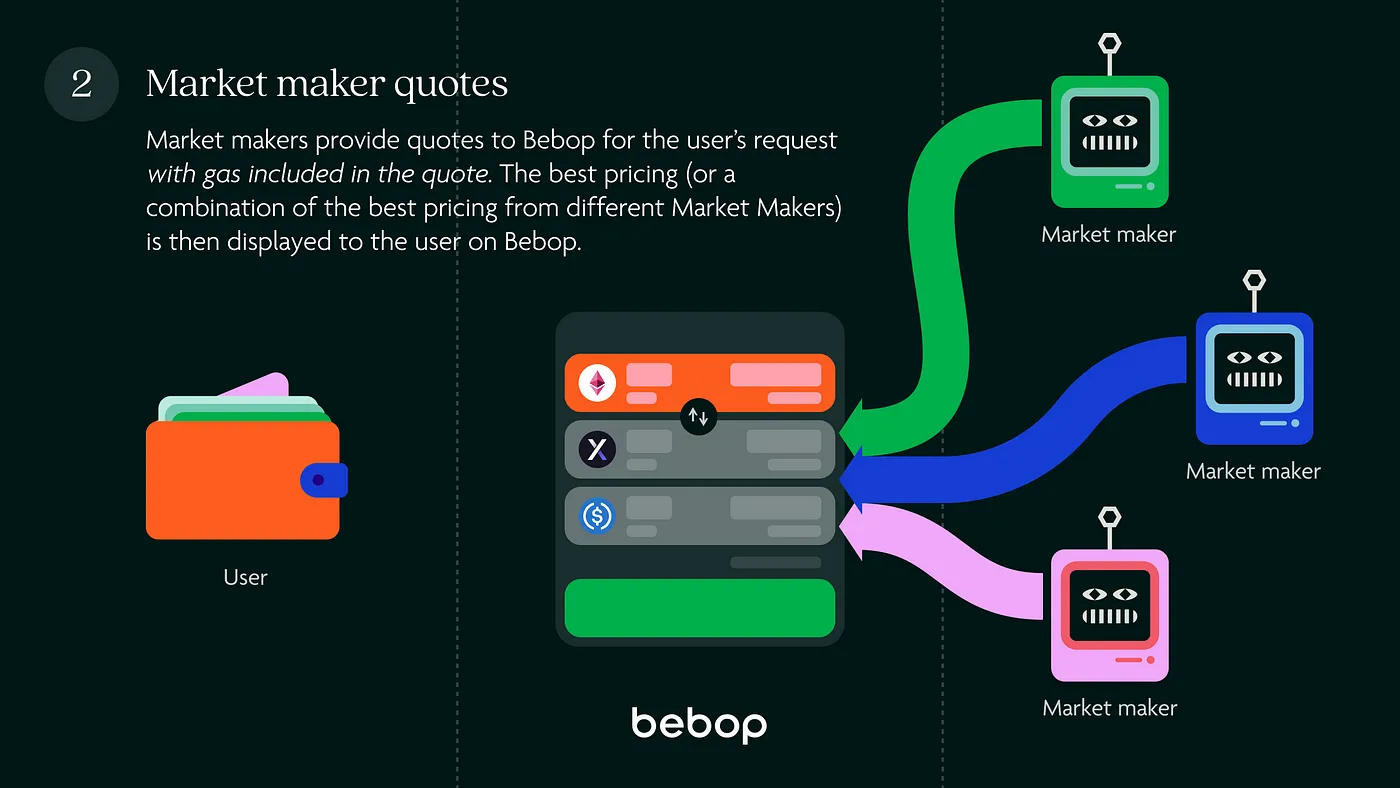
Step 2: Market maker quotes#
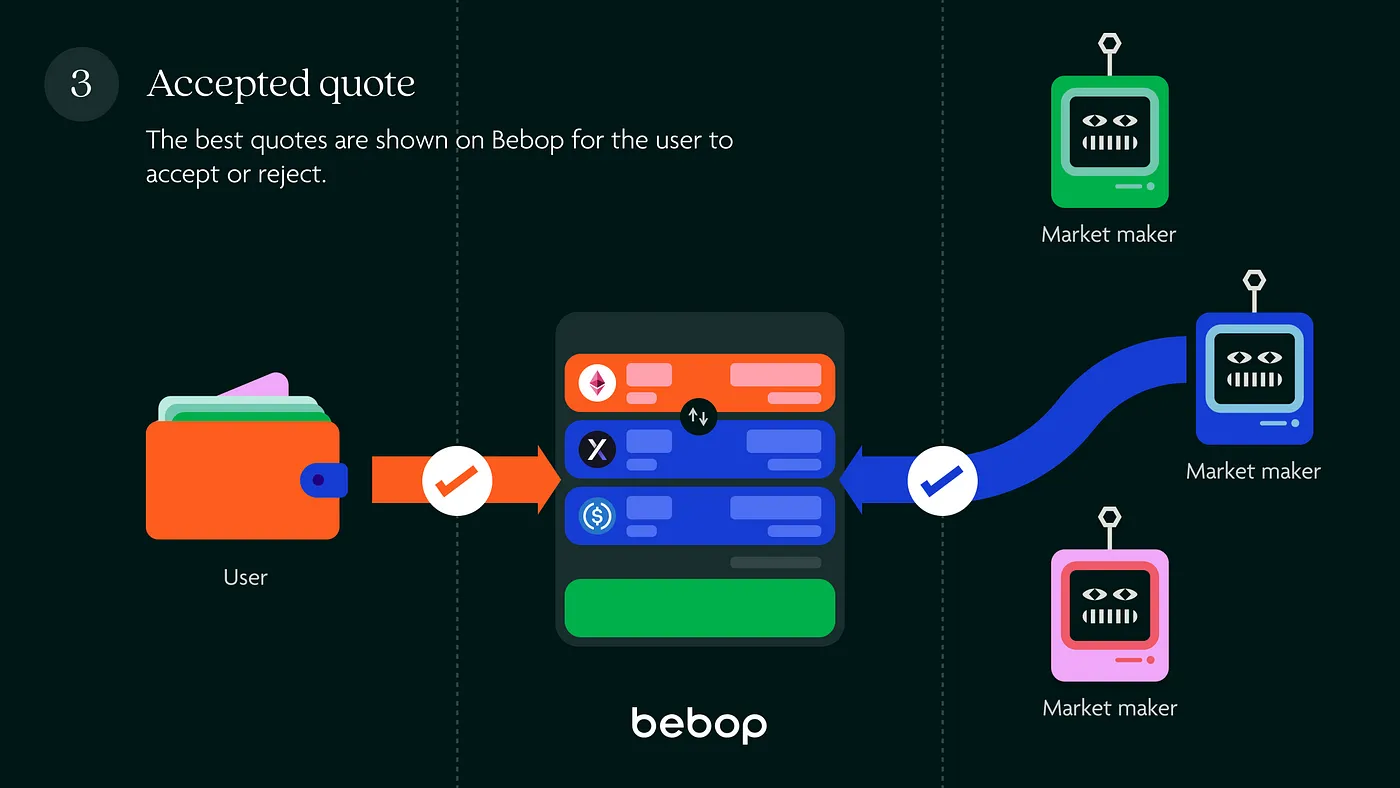
Step 3: Accepted quote#
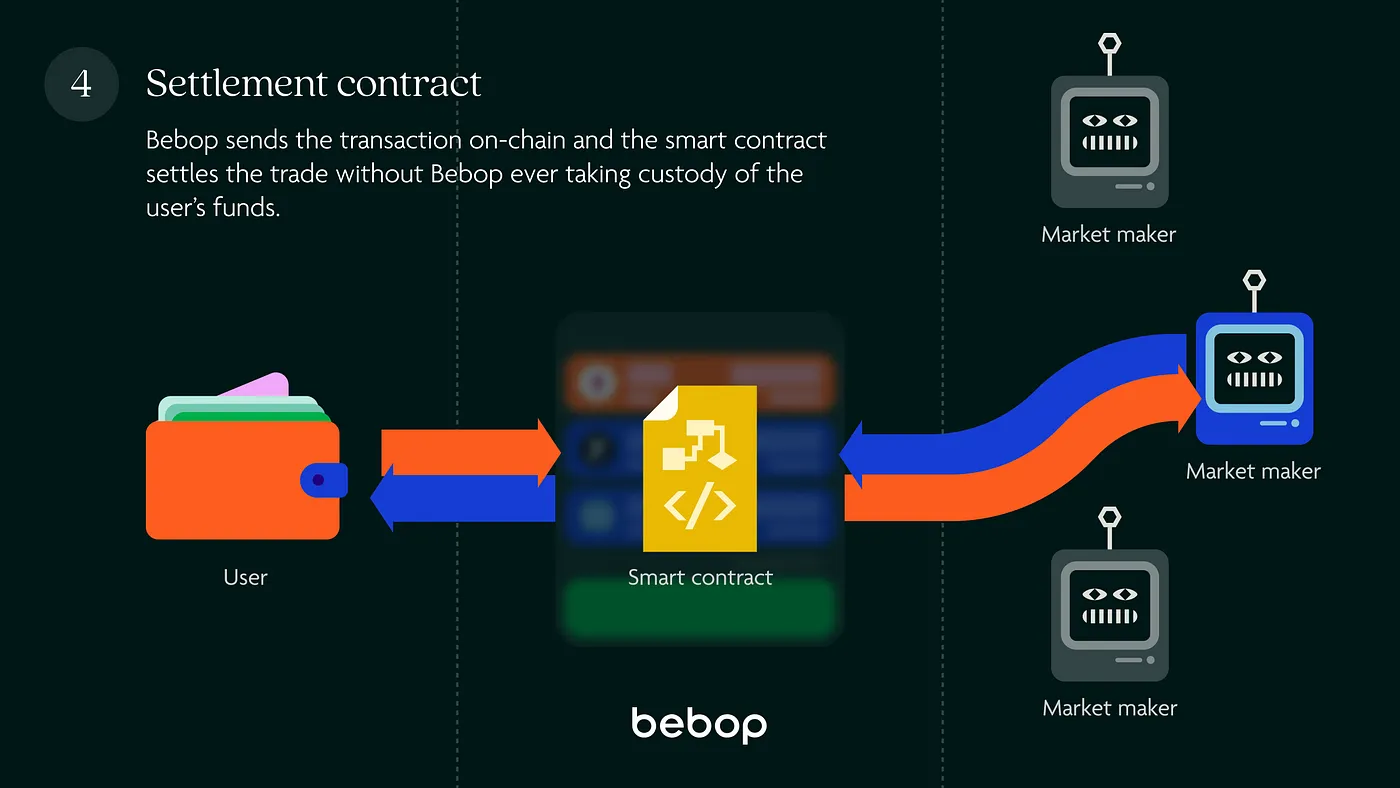
Step 4: Settlement contract#
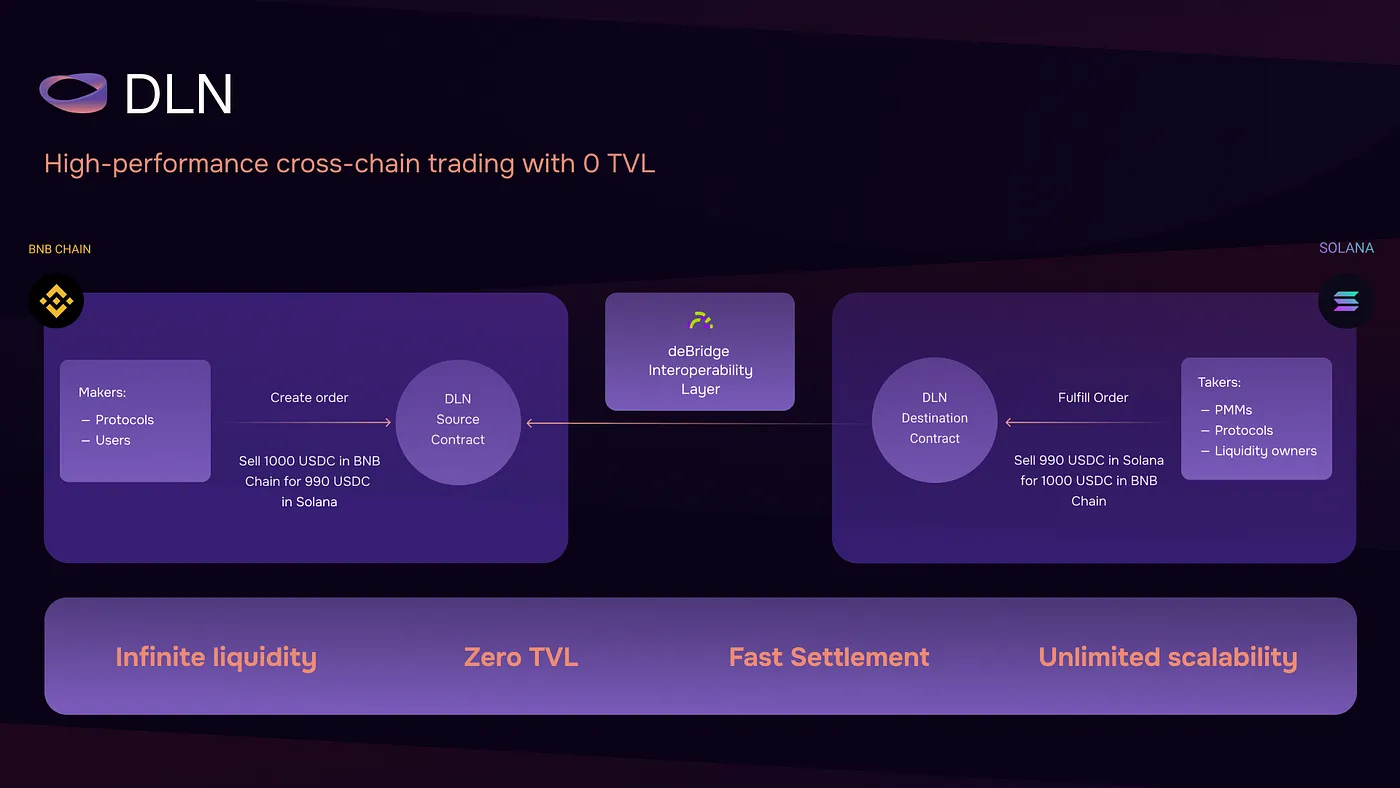
DLN: CROSS-CHAIN MEETS HIGH PERFORMANCE
The DLN protocol layer acts as a set of smart contracts that work like digital assistants for anyone on the blockchain (called a Maker). Makers can use these smart contracts to create limit orders for trades between different blockchains.
Here’s how it works: When a Maker creates an order, they put in a certain amount of a digital asset on one blockchain and specify the details, like which token and how much they want on another blockchain. The DLN smart contract locks this amount on the first blockchain temporarily. Now, anyone on the second blockchain (called a Taker) with enough digital assets can try to fulfill the order. Once the Taker successfully does this, a message is sent back to the first blockchain through a special messaging system. This message unlocks the funds on the first blockchain, and the Taker gets the digital assets. That’s how the DLN protocol helps complete these cross-chain trades.
In conclusion, RFQ-based DEXes bring a breath of fresh air to the world of decentralized trading. By allowing users to request quotes and choose the best prices, these platforms make the trading process straightforward and tailored to individual needs.
The transparency inherent in the RFQ model ensures that users know exactly what they are getting into, avoiding surprises with fluctuating prices. Moreover, the cost-effectiveness is noteworthy, with gas fees often included in the quoted price, streamlining the entire transaction process. In essence, RFQ-based DEXes offer users not just a platform but a user-centric experience, where simplicity, transparency, and cost-effectiveness reign supreme in the decentralized trading landscape.