
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we think about financial transactions and data security. However, as with any technology, it comes with its challenges, one of the most significant being scalability.
As blockchain networks grow in popularity and adoption, they face scalability issues. With an increasing number of transactions, the network becomes congested, leading to slower transaction times and higher fees during peak periods. Overcoming these bottlenecks is crucial for blockchain technology to achieve mainstream adoption and handle the demands of a rapidly growing user base.
This is where ZK Sharding comes into play.
But what is ZK Sharding?#
To grasp the concept of ZK Sharding, we need to understand two key components: Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) and Sharding.
A. Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs)#
Zero-Knowledge Proofs are a cryptographic method that allows one party to prove to another that they know specific information without revealing any details about that information. It's like proving you know a secret without actually revealing the secret itself.
B. Sharding#
Sharding, on the other hand, is a database partitioning technique that breaks data into smaller, more manageable pieces, or 'shards'. Each shard contains a unique set of data and operates independently, allowing for parallel processing of transactions.
ZK Sharding: Combining ZKPs and Sharding
ZK Sharding is a novel approach that combines Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) and Sharding to enhance blockchain scalability. By processing multiple transactions simultaneously across different shards while ensuring security and privacy through ZKPs, ZK Sharding allows for increased transaction speed and throughput.
A real-world example of ZK Sharding in action is the Nil Foundation's rollup network, which leverages ZK Sharding to process transactions quickly and securely.
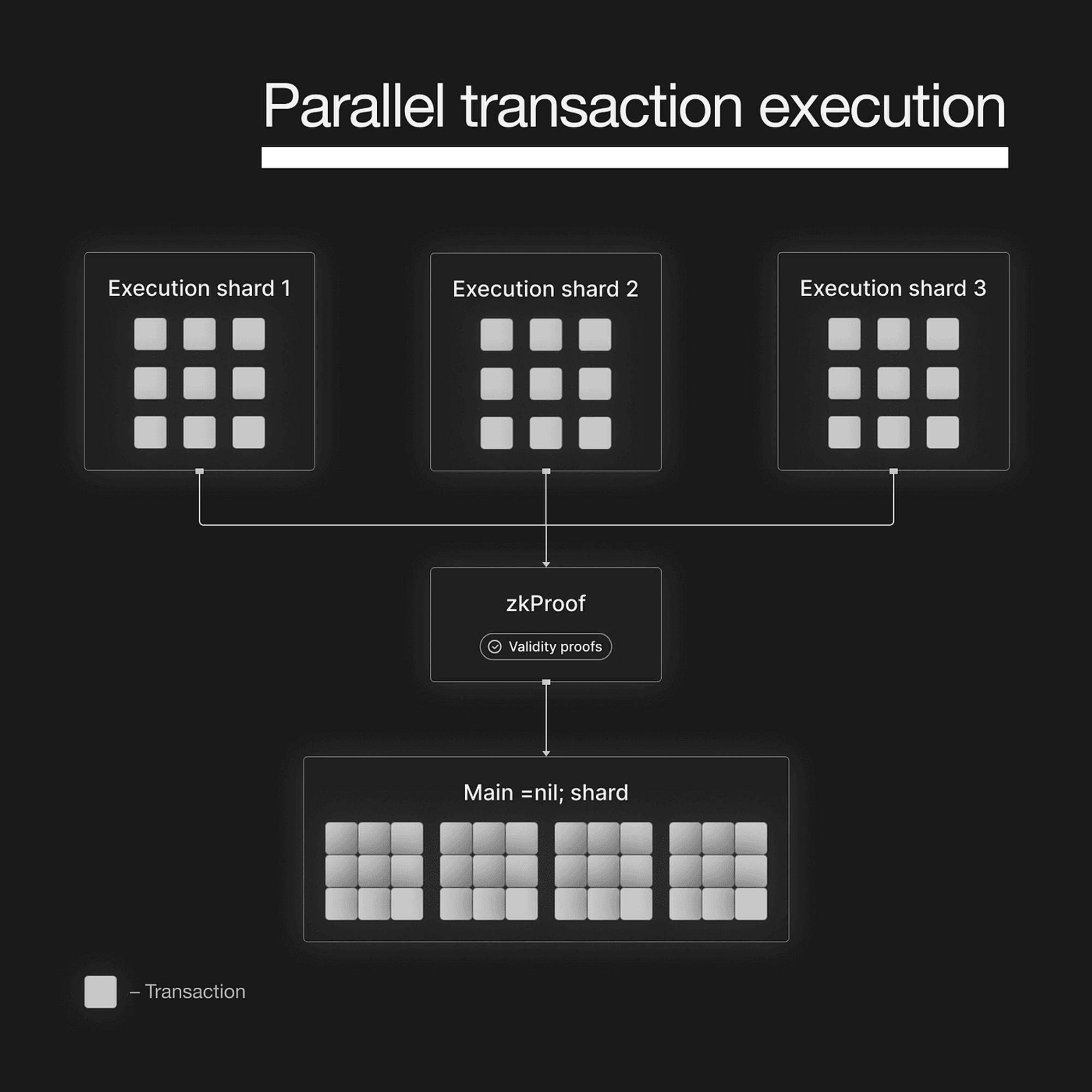
But, why is scaling Ethereum is imp?#
Scaling Ethereum is crucial for achieving mass adoption and transforming it into a truly global platform for decentralized applications (DApps) and transactions. Currently, Ethereum processes around 15-20 transactions per second (TPS), which falls short of meeting the demands of a rapidly growing user base.
Imagine a city with narrow roads - traffic jams are inevitable. Similarly, with limited TPS, Ethereum experiences congestion, resulting in slower transaction times and higher fees during peak periods. To become a mainstream platform for various applications, including finance, gaming, and more, Ethereum needs to boost its TPS significantly. The adoption of ZK Sharding and similar scaling solutions becomes pivotal in paving the way for a smoother, faster, and more accessible Ethereum network.
What are the challenges of scaling Layer 1?#
Blockchains undertake three essential functions:
- Execution
- Security (or consensus)
- Data availability.
However, monolithic blockchains attempting to handle all three tasks simultaneously encounter limitations, as evident in the blockchain trilemma.
A. Blockchain Trilemma: Execution, Security, and Data Availability#
Monolithic blockchains face a predicament outlined by the blockchain trilemma, where all nodes must store the entire ledger state or have a reliable mechanism for ensuring validators publish complete blockchain data. This necessity arises because validators and full nodes must verify that proposed blocks adhere to blockchain rules, such as excluding invalid transactions.
B. Storage Dilemma and Monolithic Blockchains#
The demand for validators to possess ample disk space, processing speed, and memory constrains their scalability. To address this, enhancing throughput at the base layer involves adjusting block production speed and size, necessitating considerations such as increasing slots per epoch and raising the block gas limit.
C. Leveraging Throughput at Layer 1#
Increasing throughput at Layer 1 relies on strategic adjustments to block production speed and size. For Ethereum, enhancing block production speed entails augmenting the number of slots per epoch, a measure that may require a faster consensus mechanism to maintain liveness. Additionally, expanding block size involves raising the block gas limit, presently set at 30 million.
Current Scaling Solutions: Layer 2 and Rollups#
Scaling solutions, such as Layer 2 (L2) solutions and rollups, have emerged as crucial advancements in addressing Ethereum's scalability challenges. These solutions aim to elevate the transaction processing capabilities of the Ethereum network beyond the limitations posed by its Layer 1.
A. Moving Execution Off-chain while Preserving Integrity#
ZK-rollups, a specific type of rollup, ingeniously move the execution of transactions off-chain while preserving the integrity of the blockchain. The incorporation of data compression and validity proofs enables these solutions to significantly enhance the throughput and efficiency of Ethereum, offering a practical means to scale without overburdening the main chain.
B. Drawbacks: Off-chain Verification and Centralized Sequencers#
Despite their promising scalability benefits, scaling solutions like L2s and rollups come with certain drawbacks. One notable challenge is the reliance on off-chain verification, where the computational work is performed away from the main chain, introducing potential trust issues. Additionally, some scaling solutions involve centralized sequencers, which could compromise the decentralized ethos of blockchain networks.
Sharding and Its Role in Scaling Ethereum#
Sharding is a smart partitioning technique employed to efficiently distribute the computational and storage workload across a decentralized network, such as a peer-to-peer (P2P) blockchain system. The primary goal is to prevent each node from bearing the entire burden of handling the transactional load for the entire network.
A. Distributing Computational and Storage Workload#
In the context of blockchain projects, particularly those exemplified by the Ethereum network, sharding involves breaking down vast data tables into more manageable and distinct chunks known as shards. Each shard maintains its own unique set of data, contributing to the decentralization of the ledger.
B. Ethereum's Sharding Use Case and dApp Ecosystem#
Ethereum's ambition extends beyond creating a new form of currency; it envisions a platform capable of hosting and managing a wide array of decentralized applications (dApps) across various industries. However, the current limitations in Ethereum's capacity to store and secure massive amounts of data pose challenges. Sharding steps in as a promising solution, allowing Ethereum to scale its programs and accommodate additional data, facilitating the growth of its ecosystem.
Combining Sharding and Zero-Knowledge Proofs#
In conjunction with sharding, Zero-Knowledge (ZK) proofs, particularly in the context of ZK-rollups, play a crucial role in fortifying the security and privacy aspects of blockchain networks. ZK proofs provide a cryptographic means of validating the correctness of off-chain transactions without exposing sensitive information, enhancing the overall integrity of the system while preserving user privacy. The collaboration between sharding and ZK technology creates a powerful synergy where sharding optimizes the network's operational capabilities, and ZK proofs contribute to a trustless verification process.
Unlocking Ethereum's Potential with zkSharding#
A. Revolutionizing Scalability with Nil Foundation's zkSharding#
The Nil Foundation introduced zkSharding, a revolutionary zkRollup solution that promises to catapult Ethereum's scalability to unprecedented levels, exceeding 60,000 transactions per second (TPS). Positioned as a dynamic sharding mechanism, zkSharding seamlessly combines zkRollup with dynamic sharding, enabling horizontal scalability without sacrificing the benefits of a unified execution layer.
B. Unified Execution, Security, and Functionality#
Nil Foundation pioneers a unified execution environment that eliminates concerns related to security and liquidity fragmentation. With each shard integral to the entire cluster, the need to migrate liquidity from Ethereum is significantly reduced. Security is fortified through zkEVM compiled via zkLLVM, ensuring auditable security with easily inspectable code. The commitment to decentralization is ingrained from day one, facilitated by the decentralized proof generation enabled by Nil Proof Market.
C. Differences from Other Sharding Solutions#
Nil Foundation's zkSharding employs cross-shard communication, allowing for quicker transaction execution compared to systems that rely on communication through a central hub. This innovative approach is seamlessly integrated into the overall protocol, as opposed to being managed by separate bridges. Each committee has additional tasks beyond maintaining their shard, such as tracking cross-shard messages within near-shards and providing fraud-proofing by not relaying a cross-shard transaction.
Components of zkSharding Mechanism#
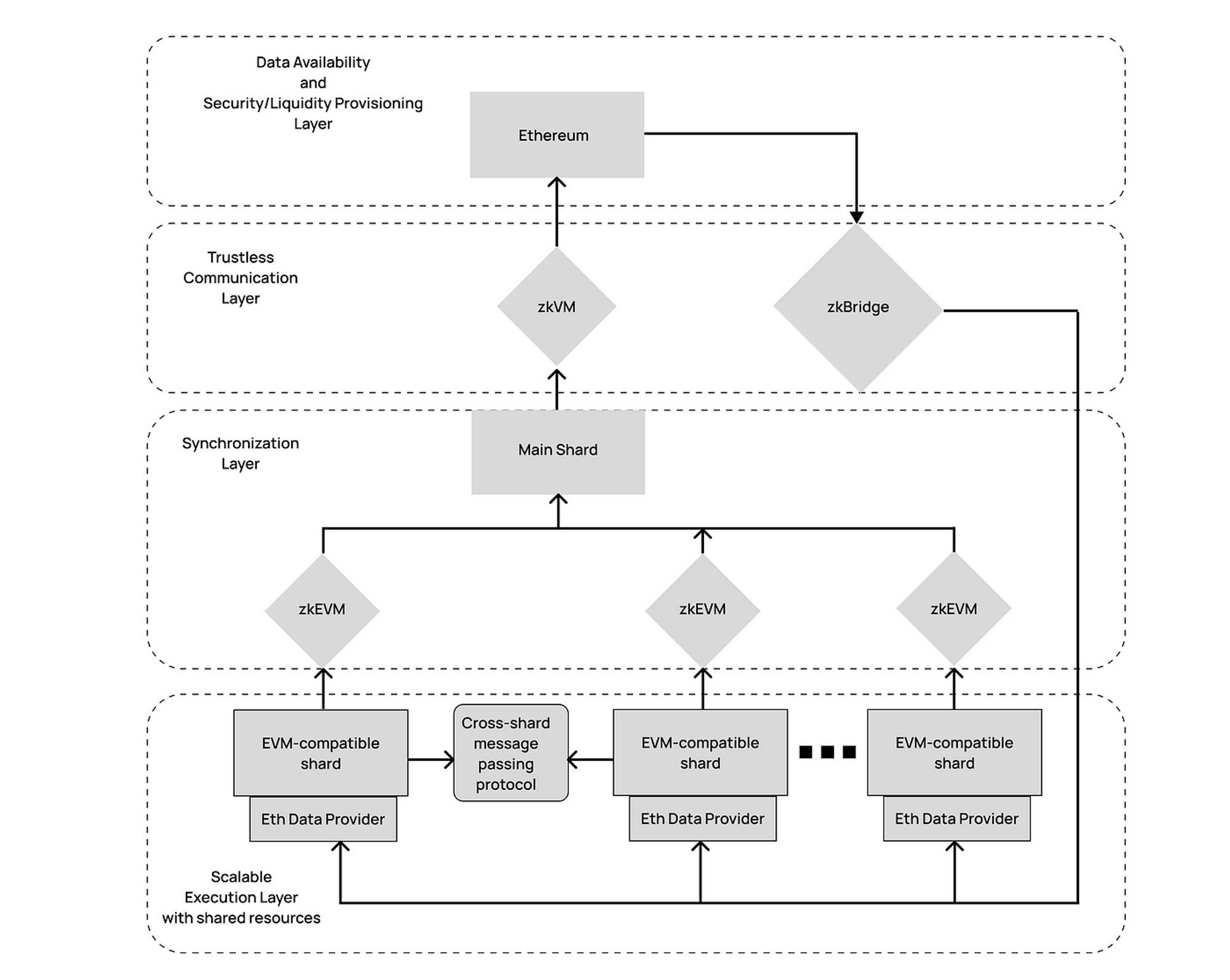
A. Dynamic Sharding#
Dynamic sharding addresses challenges in Ethereum's application-level sharding by introducing protocol modularity, where each application has its own database. Nil zkSharding revolutionizes this paradigm with a protocol-level, enshrined sharding solution. In this dynamic system, each shard collaborates seamlessly within a unified protocol, eliminating the need for dedicated bridges.
- Protocol Modularity and Shard Collaboration Each application has its own database, but shards collaborate within a unified protocol, eliminating the need for dedicated bridges.
- Primary Shard and Its Roles The first shard, known as the "primary shard," holds essential data about the protocol's consensus, current parameters, data about other shards, and hashes of the most recent replication packets (blocks) from all shards. It sets the protocol's rules, parameters, and ensures synchronization across all other shards.
- Secondary Shards and Account Distribution Secondary shards specialize in processing user transactions, managing specific subsets of tables based on a deterministic function of the account's public key and shard metadata.
- Split and Merge Conditions for Efficient Resource Allocation Shards dynamically split into two when their occupancy approaches capacity, and merge when their occupancy remains substantially below capacity, ensuring efficient resource allocation.
B. Cross-Shard Communication#
In Nil Foundation's sharding framework, all accounts are distributed across various shards, but cross-shard communication is seamlessly integrated directly into the overall protocol, eliminating the need for separate bridges.
- Integrated Within the Protocol Cross-shard communication is integrated within the overall protocol, not managed by separate bridges.
- Accountability Through Fraud Proofing and Slashing The system introduces the possibility of providing fraud proofs for not relaying a cross-shard transaction, ensuring validators who neglect their responsibility can be penalized or "slashed."
zkLLVM: Enabling Developer Accessibility#
A. Understanding LLVM and Its Role#
LLVM (Low-Level Virtual Machine) is a compiler infrastructure that facilitates the development and optimization of programming languages, providing a robust foundation for generating efficient machine code for various architectures.
B. zkLLVM: Translating Languages for Circuit Compatibility#
zkLLVM is a special translator that takes programming languages like C++ and Rust and turns them into a format that can be proven correct in special systems called circuits. It directly translates the original program without adding extra layers or slowing down the process, making it efficient for specific virtual machines.
C. Benefits of zkLLVM: Efficiency, Compatibility, and Accessibility#
Unlike other methods, zkLLVM doesn't add any extra layers or make things slower; it's like having a direct route from your program to the special circuit without any detours. Additionally, because zkLLVM is based on LLVM, it works with any computer language that uses LLVM, making it flexible and compatible.
Conclusion#
Nil Foundation's groundbreaking work on zkSharding introduces a transformative approach to Ethereum's scalability challenges. By dynamically sharding the blockchain and seamlessly integrating cross-shard communication within the protocol, zkSharding eliminates the need for external bridges, fostering efficiency and security.
The utilization of zkRollups, along with a unique protocol-level enshrined sharding design, ensures horizontal scalability without compromising the benefits of a unified execution layer. With the ability to handle a vast number of transactions per second, efficient resource allocation through dynamic sharding behaviors, and the elimination of fragmentation challenges, zkSharding positions itself as a key player in the evolution of blockchain technology.
As Ethereum continues to grow and attract diverse applications, zkSharding presents itself as a crucial innovation that can unlock the full potential of decentralized applications, paving the way for a more scalable, secure, and interconnected blockchain ecosystem. The foundation laid by Nil in building zkSharding points towards a future where Ethereum can truly achieve mass adoption and emerge as a robust, high-performance blockchain platform.