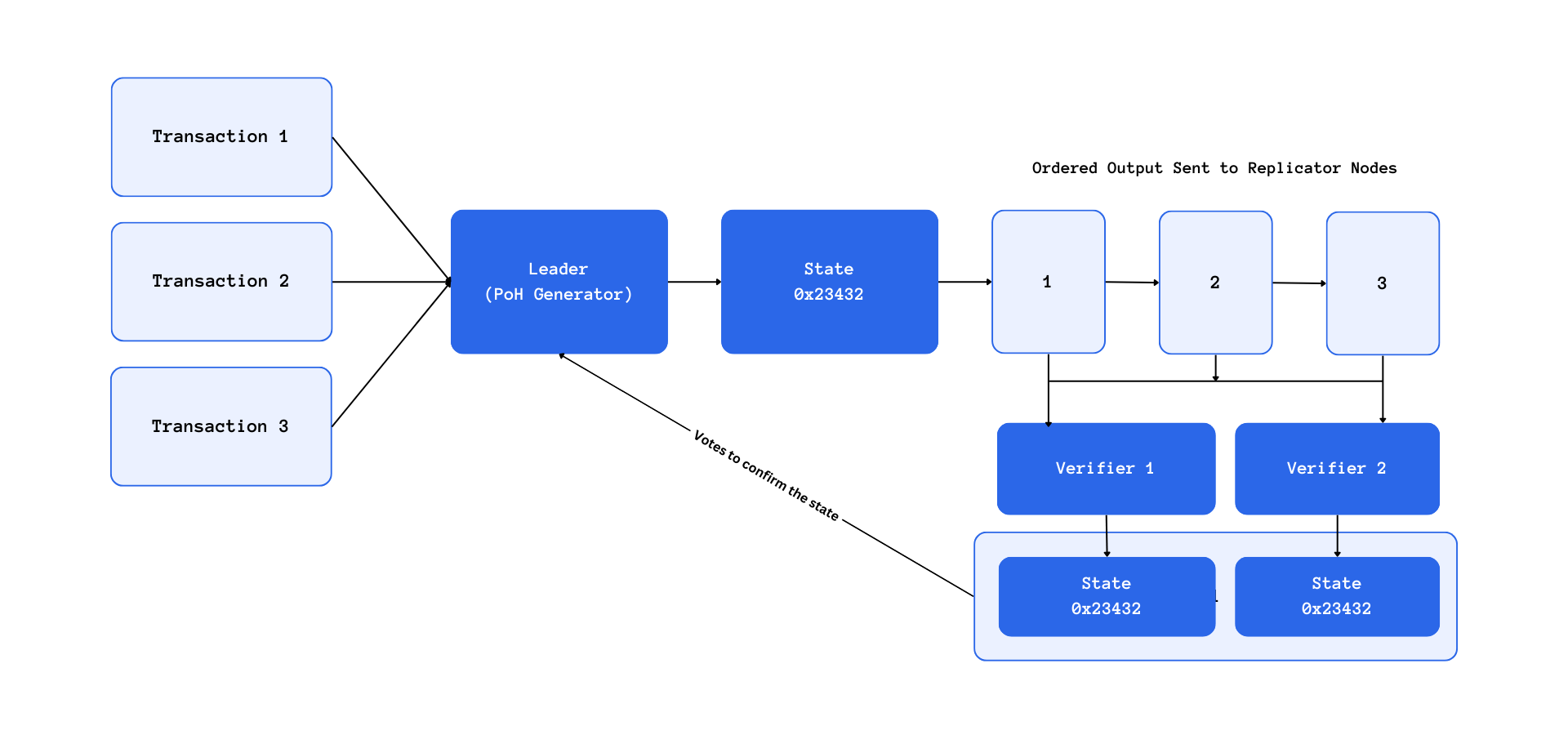
 Solana stands out in the blockchain space with its unique approach to data storage and transaction execution. In Solana, all data are stored in accounts, and programs are designed to be stateless, interacting with accounts to manage state. This architectural choice is pivotal in allowing Solana to optimize the utilization of available resources and enhance transaction processing efficiency.
Solana stands out in the blockchain space with its unique approach to data storage and transaction execution. In Solana, all data are stored in accounts, and programs are designed to be stateless, interacting with accounts to manage state. This architectural choice is pivotal in allowing Solana to optimize the utilization of available resources and enhance transaction processing efficiency.
Parallel execution#
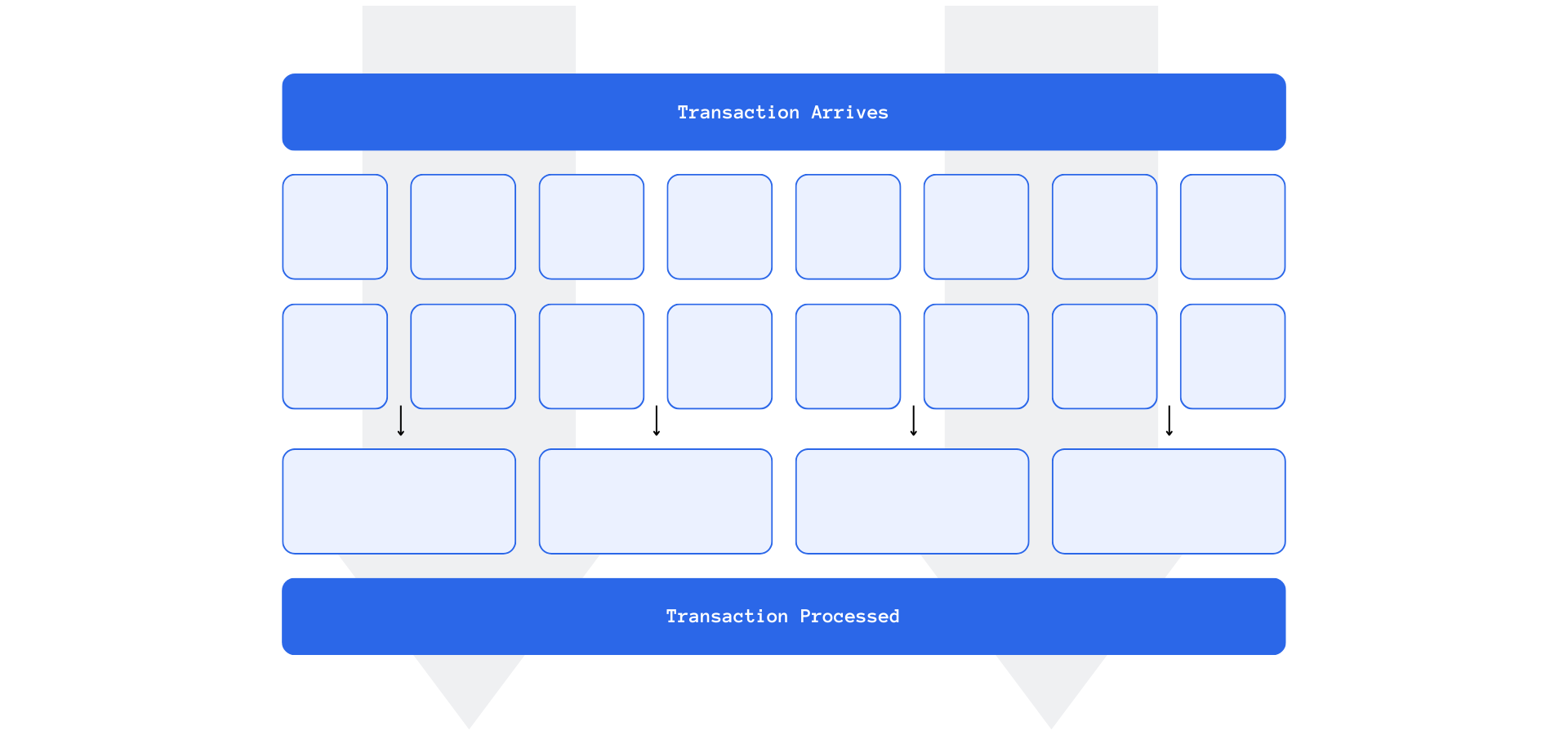
Solana leverages parallel execution to expedite transaction execution and finalization by maximizing the use of available resources within the blockchain. Transactions in Solana are composed of a list of instructions interacting with accounts, either in a read or read-write mode. This structure enables Solana’s Sealevel runtime to determine the sequence of transaction execution and identify transactions that can be executed in parallel efficiently.
- Transaction Division and Execution: By applying set theory, transactions are sorted into various sets based on the accounts they interact with and the required permissions. This categorization allows each set to have its designated lane, with multiple transactions in a lane executed sequentially, while different lanes are processed in parallel.
- Optimized Resource Utilization: Solana’s knowledge of account interactions within transactions facilitates optimal utilization of parallelism, maximizing resource efficiency.
Streaming Transactions and Efficiency
Solana’s absence of a mempool is another distinctive feature, with transactions being directly streamed to the leader. This approach eliminates the need for storing unconfirmed transactions, streamlining the transaction processing pipeline and reducing latency.
Localized Fee Markets#
Solana's utilization of parallel transaction execution isn't just a feat of enhancing speed and efficiency; it's also a gateway to implementing localized fee markets, a breakthrough that brings about nuanced financial interactions within the blockchain. This implementation allows Solana to maintain a balanced and equitable fee structure, ensuring that surges in transaction demand in one area don’t unjustly impact the entirety of the network.
Impact of Parallel Execution on Fee Markets
Parallel execution enables Solana to isolate and manage transaction fees with precision. For instance, during a minting process on Solana, where bots may be generating a flurry of high-priority transactions, the heightened demand for block space for a specific account doesn’t indiscriminately drive up the fees across the network. Instead, Solana can increase the gas for the involved account or program, leaving others unaffected and maintaining normal execution in different lanes.
- Localized Adjustments: This capability to make localized adjustments to gas fees means that other accounts or programs remain unaffected by the high demand in a particular segment, maintaining equilibrium in the fee market.
- Streamlined Execution: Parallel execution and strategic account structuring in Solana create an environment where each account or program can operate in its microcosm, enabling precise adjustments and ensuring the stability of the broader ecosystem.
Solana's approach makes predicting the fee market notably more straightforward and accurate. Observers can focus on program/account congestion to anticipate fees, avoiding the need to monitor the entire blockchain for transaction hotspots. This localized view of transaction interactions offers a granular perspective on network activities, allowing for more accurate and user-friendly fee predictions.
- Enhanced Predictability: This method enhances fee predictability, allowing users to anticipate transaction costs with greater accuracy and reliability, based on localized network activities.
- User-Friendly Interaction: The ability to predict fees with enhanced accuracy contributes to more user-friendly interactions within the network, allowing users to navigate the blockchain with increased ease and confidence.
Transaction Finality Speed#
Solana has been structured with a keen emphasis on achieving high-speed transaction execution, an attribute that it attains through an amalgamation of parallel execution, localized fee markets, and a unique account structure. These components harmoniously work together allowing Solana to support shorter block times, driving up its efficiency and throughput.
Speed and Structure
Each slot in Solana is designated a 400ms window, within which a block needs to be published. This restricted timeframe necessitates a high-speed, efficient execution mechanism to ensure timely block publication. Furthermore, Solana’s blocks have a larger size compared to Ethereum, allowing for the incorporation of more transactions in each block.
- Fast and Efficient: The combined benefit of quicker block speed and increased block size allows Solana to rapidly incorporate and execute transactions, outpacing many of its contemporaries in transaction finality speed.
- Optimized Execution: Solana's focus on optimizing execution processes supports the seamless addition of transactions into blocks, showcasing its commitment to speed and efficiency.
Transaction Finality and Consensus Mechanism
Despite its speed, Solana also operates on a probabilistic consensus algorithm, meaning that a transaction's inclusion in a block doesn’t immediately finalize it. However, once a transaction or block is confirmed 32 times, achieving an age of 32 blocks, it is considered finalized and irreversible.
- Soft Finality and Finalization Time: In practical terms, this means Solana can achieve soft finality in less than a second and finalization in approximately 12.8 seconds, significantly reducing the wait time for transaction confirmations and enhancing user experience in transaction interactions.
PoS#
Solana’s Proof of Stake (PoS) system has been meticulously engineered to provide optimal availability and efficiency, establishing it as a robust and reliable platform in the blockchain ecosystem. A core part of this design is Solana’s blending of PoS with Proof of History (PoH), harmonizing the advantages of both to provide enhanced service to its ecosystem.
Availability and Network Strength
As of September 2023, Solana operates with approximately 3000 nodes. This substantial number of nodes is indicative of the robustness and resilience of the Solana network, ensuring its constant availability and uninterrupted service to users.
- Node Diversity: The substantial and diverse array of nodes underlines Solana's commitment to maintaining network availability and adaptability, ensuring uninterrupted and reliable service.
Diversity in Client Implementation
In its continual pursuit of development and optimization, Solana hosts three client implementations: the Solana Labs client developed in Rust, the Jito client, a fork of the Solana Labs client with additional features, and the Firedancer client, currently under development and built using C programming language.
- Continual Development: This diversity in client implementation signifies Solana's commitment to innovation and adaptability, fostering an environment conducive to ongoing development and enhancement.
Consensus Mechanism: A Synchronized Approach
Solana's consensus mechanism is a unique amalgamation of PoS and PoH, with PoS facilitating leader rotation and transaction confirmation, and PoH providing a globally synchronized clock to verify the ordering of transactions.
Efficient Transaction Confirmation: The synergy between PoS and PoH allows Solana to achieve soft confirmation in approximately 1 second and finalization in roughly 12.8 seconds, optimizing the transaction confirmation process and enhancing user experience.
Solana Pay
Solana Pay stands out as a transformative payment infrastructure within the solana ecosystem, focusing on user-centric designs and functionalities by combining rapid and reliable transaction processes with advanced features like account abstraction and QR-based transactions,
QR-Based Transaction Mechanism
Solana Pay functions by generating QR codes based on predetermined parameters, which can be effortlessly scanned using any compatible wallet. This methodology is indicative of Solana's approach to simplify user interaction within its network, reflecting its drive to optimize user experience.
- Transaction Reference and Confirmation: Each transaction facilitated through Solana Pay has a distinct reference attached to it, identified by a public key. This reference enables the easy location and matching of the on-chain transaction made by the wallet with the QR code, allowing applications to display a “success” screen promptly, enhancing the user's interaction with the system.
-

Stablecoins#
Solana stands out by offering native support for major stablecoins like USDC and USDT. This native integration enhances efficiency and accessibility for users within the Solana ecosystem. Transactions with these stablecoins benefit from Solana's high-performance infrastructure, boasting impressive transaction speeds and low fees.
User experience#
Solana’s approach to payments currently stands as one of the most user-friendly and efficient within the blockchain sector. It delivers rapid transactions coupled with faster finalization confirmations and extensive stablecoin support, establishing itself as a preferred solution for payments, alongside several other Layer 1 and Layer 2 projects.
- Fast, Reliable, and Inclusive: Solana’s inherent speed and extensive stablecoin support make it an optimal choice for users seeking fast and reliable payment solutions, with its platform being inclusive and accommodating a broad spectrum of transaction needs.
- Account Abstraction Features: Solana incorporates advanced account abstraction features, emphasizing its commitment to providing a seamless and sophisticated user experience, allowing users to interact with the blockchain in a more intuitive and streamlined manner.
Conclusion#
In contrast, Layer 1 solutions like Solana, with their architectural innovations and enhanced transaction finalities, present themselves as more viable alternatives, specifically tailored for payments. These platforms, characterized by their inherent efficiencies and strategic approach to transaction processing, seem to have surpassed their counterparts in aligning with the requisites of a payments-oriented blockchain at this juncture.
In conclusion, while the blockchain space is brimming with innovations and possibilities, discernment and vigilance are paramount. The continuous evolution of platforms brings forth new horizons in blockchain application for payments, yet the selection of a blockchain solution necessitates a careful evaluation of its intrinsic capabilities and the alignment of its features with the specific demands of payment processing.